Cervical Cancer :
Cervical cancer affects the entrance to the womb. The cervix is the narrow part of the lower uterus, often referred to as the neck of the womb. Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the cells that protects the Cervix - the lower part of the uterus (womb) that connects to the vagina (birth canal). Cervical cancer occur when cells change in women’s cervix and starts to grow on the surface of the Cervix. This cancer can influence the inner tissues of the cervix, grow beyond control, and may largely spread to other parts of the body like lungs, liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum.
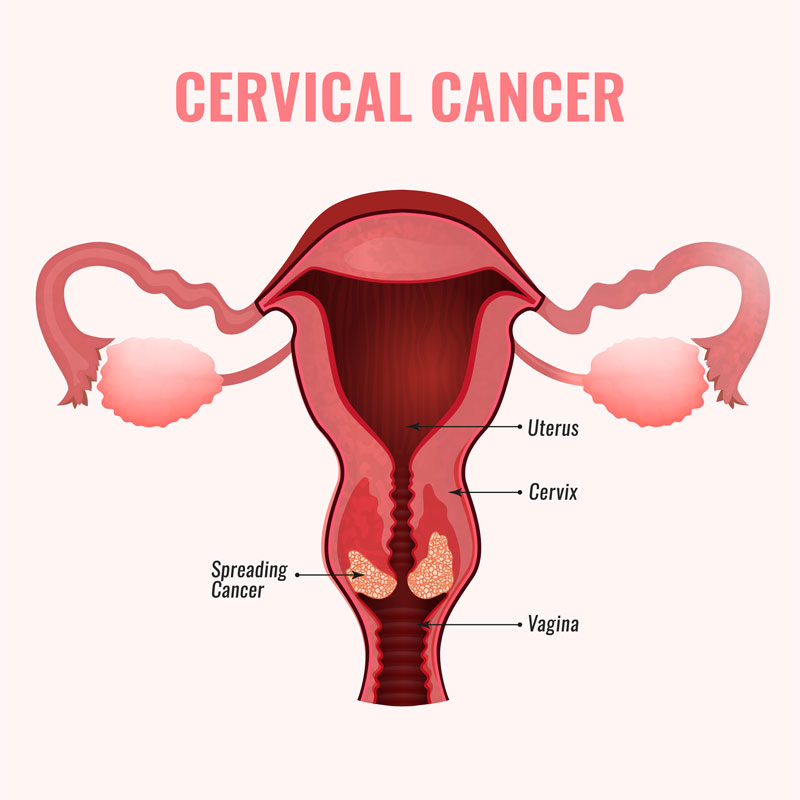
Types of Cervical Cancer :
The main types of cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Causes of Cervical Cancer:
Cervical cancer starts with abnormal changes in the tissue. Many cases with Cervical Cancer are connected to the infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Different types of HPV can cause genital warts, skin warts, and other skin disorders. Others are linked to cancers involving the vagina, penis, anus, tongue, and tonsils.
HPV can also cause other cancers in women and men which include:
Signs and symptoms :
Early cervical cancers and pre-cancers don’t show symptoms in women. Symptoms are seen when the cancer grows in size and spread into nearby tissue.
The most common symptoms for the Cervical Cancer spread are:
Signs and symptoms seen with more advanced disease can include:
If you have any of these symptoms, seek a health care expert immediately. If you ignore these symptoms, then the cancer may reach an advanced stage which may lower the chances for successful treatment.
Stages of Cervical cancer :
The diagnosis for Cervical Cancer will show the stage and level of Cancer spread in the Cervix or in the nearby areas. Based on the staging report of Cervical Cancer, the Onco Expert will give a suitable treatment for the patient.
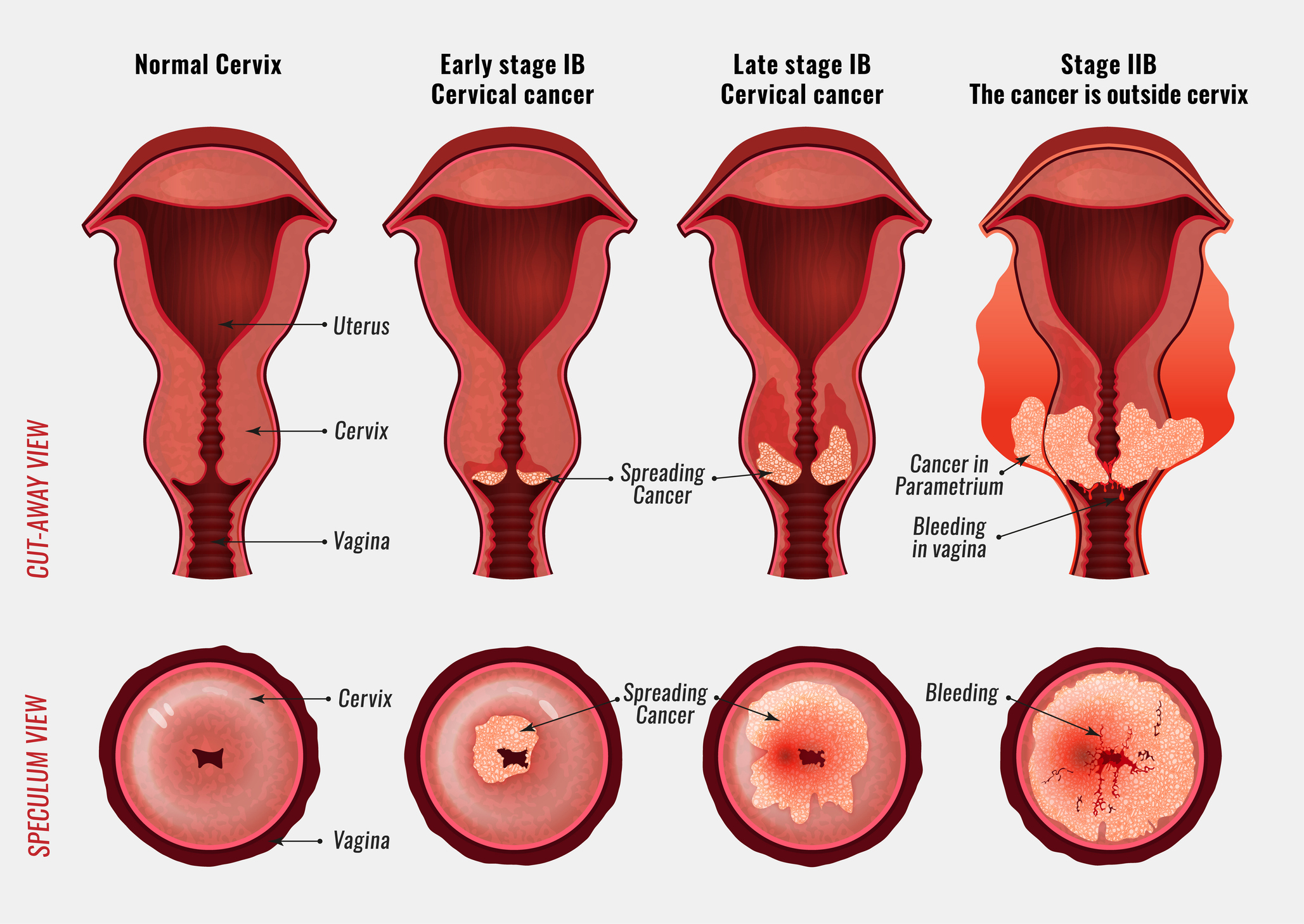
Cervical cancer has four stages:
Stage 1 :
The size of the cancer is small, and it may have spread to the lymph nodes but hasn’t spread to the other parts of the body.
Stage 2 :
The size of the cancer is large and may have spread outside of the uterus and cervix or to the lymph nodes but still hasn’t extended to the other parts of the body.
Stage 3 :
The cancer may have spread to the bottom of the vagina or to the pelvis and may block the ureters (tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder) and also has not spread to the other parts of the body.
Stage 4 :
There are chances of Cancer having spread outside of the pelvis and reached to the organs like lungs, bones, or liver.
Diagnosis and Tests for Cervical Cancer:
In Cervical Cancer Screening, the Papanicolaou test (Pap smear) and high-risk HPV testing is broadly used. A Pap smear is part of a woman’s routine pelvic check-up. The doctor accumulate cells from the surface of the Cervix, and the Lab technician examines them through the microscope. If anything, unusual is spotted, then the doctor takes out a sample of cervical tissue to perform a procedure called as Biopsy.
Tests suggested by the Gynaecologist to check for cancer cells:
A) Cervical biopsy/ Colposcopy:
Colposcopy exam is performed by the doctor if unusual cells are found by Pap smear. During the Colposcopy examination, the cervix is stained with a safe dye or acetic acid so see the cells clearly. A microscope called as Colposcope is used, which enlarge the cervix by 8 to 15 times, to check for the unusual cells for biopsy. Another biopsy is required later if the signs of invasive cancer is seen in the colposcopy.
B) Cone biopsy/Conization:
The doctor even may opt for Conization procedure (removing a part of the cervix) in the Operation Theatre while the patient is under the anaesthesia. In the Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP), the doctor uses an electrified loop of wire to take a sample of tissue from the cervix. LEEP, Scalpel (cold knife conization), or a laser are normally outpatient procedures, which can release the patient from the hospital on the same day.
If the gynaecologist examines the Pap test to be abnormal or finds other symptoms of cervical cancer, then the doctor will study more about the medical history of the patient as well as of the family. The doctors may prescribe to perform more tests if they find cancer cells in the cervix, and also check the lymph nodes to see the cancer spread.
Cervical cancer treatment:
Cervical cancer can be treated if it is detected in early stages.
The four main treatments for Cervical Cancer are:
Sometimes these treatments are combined to make them more effective.
A) Surgery:
The Surgery is performed to remove maximum Cancer as possible. Sometimes the doctor removes only the area of the cervix that is affected by the cancer cells. If the cancer is drastically spread, then the Cervix and other organs in the pelvis are removed during the surgery.
B) Radiation therapy:
In Radiation therapy, high-energy X-ray beams are used to kill the cancer cells. The Radiation therapy can be implemented inside the body by the use of a metal tube placed in the uterus or vagina and also through a machine outside the body.
C) Chemotherapy:
In Chemotherapy the medicinal drugs are injected throughout the body to kill the cancer cells. Doctors give this treatment in sequence. The patient is given the Chemo for a period of time. Later the treatment is stopped to give the patient’s body, the time to recover.
D) Targeted therapy:
Targeted therapy is one of the cancer treatments in which drugs are used to target specific genes and proteins that are engaged in the development and longevity of cancer cells. Targeted therapy can affect the nearby tissue which helps cancer to grow and remain alive. These drugs target the cancer cells keeping safe the normal cells.
Drugs used in the Targeted Therapy can block or stop the signals that are transmitted for the growth of cancer cells, or can instruct the cancer cells to destroy themselves. Targeted drugs restricts the multiplication of cancer cells. In short, these drugs holds a cancer cell from splitting and developing a new cancer cell.


