Liver Cancer :
Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. The cancer that arises in the liver is called primary liver cancer. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung, or breast - and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer or secondary liver cancer.
Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) tends to occur in livers damaged by birth defects, alcohol abuse, or chronic infection with diseases such as hepatitis B and C, hemochromatosis (a hereditary disease associated with too much iron in the liver), and cirrhosis.
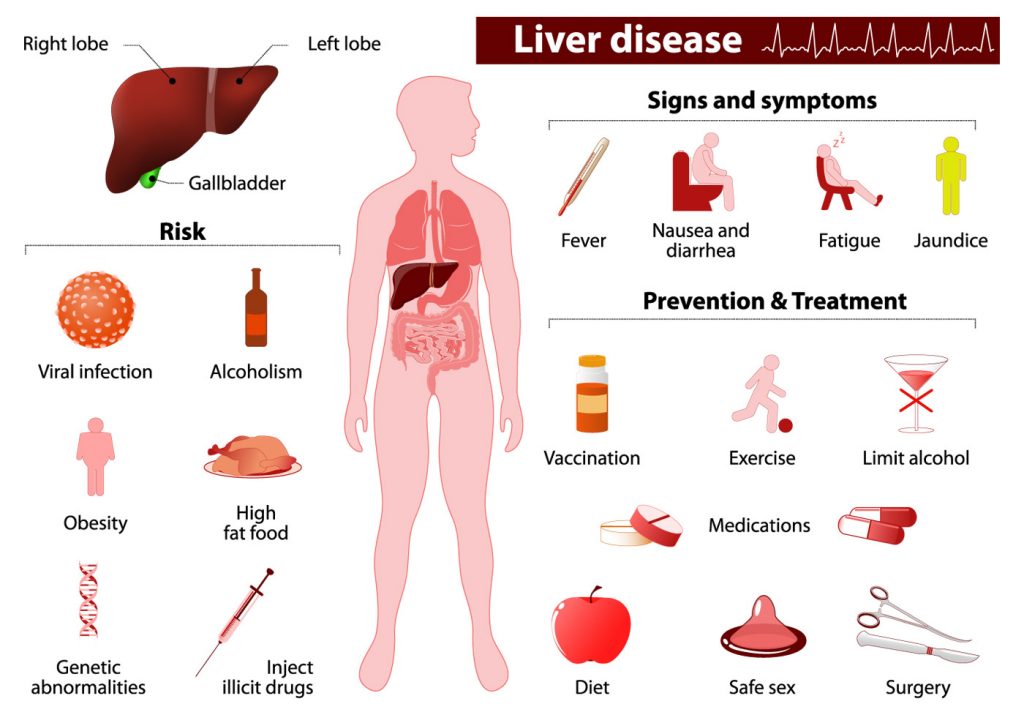
Risk Factor :
People with certain hereditary and/or rare diseases may be prone to developing liver cancer. These include:
Signs and symptoms :
People may feel to be fit in the early stages of liver cancer, but it may risk their life in the later stages. If a person experience chronic pain in the Liver, they must consult the doctor about the symptoms immediately. Delay in the diagnosis may lead to the threat of Liver Cancer.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer include:
Diagnosis :
The diagnosis of Liver cancer is done with the help of special medical tests or through a physical examination which may include CT scans, ultrasounds, and MRI.
Sometimes doctors go for liver biopsy, a procedure in which a small parts of liver tissue is removed and examined to confirm the diagnosis of liver cancer. Doctors often do genetic testing of the cancer, which helps to give the best treatment for the patient.
Stages of Liver Cancer :
To help guide treatment and define the outlook of liver cancer, healthcare professionals divide its progression into four stages:
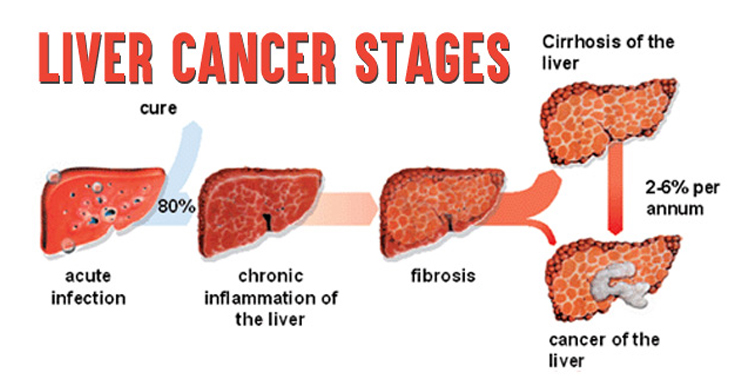
Once a doctor has diagnosed and identified the stage of cancer, a person will start to receive treatment.
Treatment of Liver Cancer :
There are various Cancer treatment recourses available for people suffering from Liver cancer. Treatments suggested by the Doctors are based on the information acquired through medical test results like the type of cancer, current stage of cancer etc.
Liver cancer treatment depends on:
If the rest of the liver is healthy and the cancer has not spread, then treatment options may include:
Sometimes the cancer may be spread within the liver. In such case the other treatments may include:
Doctors may prescribe some of the following treatments if it is still within the liver or if the cancer has spread outside of the liver, and not responding to any of the above treatments.
A surgical resection (Liver transplant) can cure Liver Cancer, but only for few patients. Nevertheless, scientists are researching with various challenging new treatments which could support to prolong the lives of patients suffering from Liver Cancer.


